ApiGateway is great service for quickly spinning up a resilient, performant API layer for your application.
An increasingly common practice, as a result of putting frameworks like NextJS, SvelteKit, and Architect behind ApiGateway on a Lambda integration, is to serve static assets, as well as data, using a single ApiGateway. The ApiGateway is assigned a Custom Domain name, and serves the web application, assets, and the api that serves the data to power it.
The Problem
When typing a url into a browser, if the protocol is not specified, most browsers will default to http. If your site is served up via ApiGateway, this will result in a failure to connect and an error:
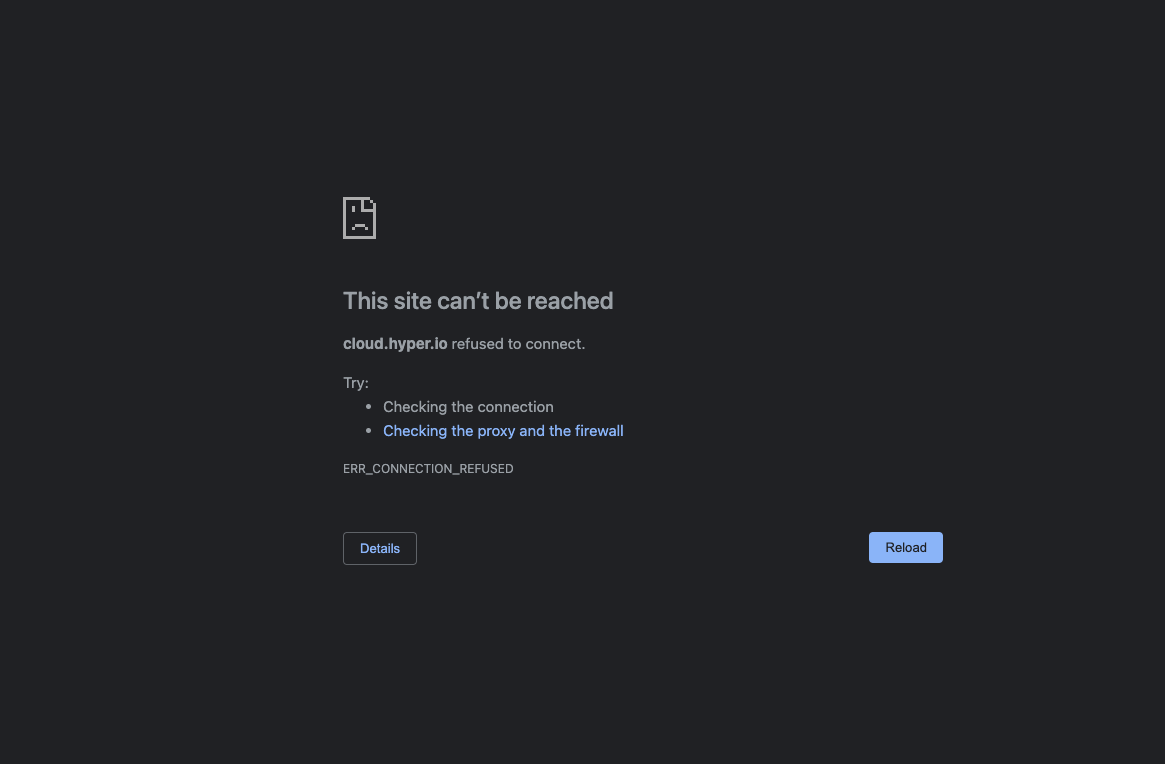
This is because ApiGateway only supports https. This isn't a great user experience. Instead of an error, it would be great to redirect http -> https.Unfortunately, this involves more moving parts than is expected. There isn't a setting that you can toggle in ApiGateway; http isn't supported. To get around this, most solutions use CloudFront to perform this redirect. There were some tutorials that already exist on how to do this, but all them were missing some key details. This post will describe how I used CloudFront in front of ApiGateway to redirect http to https.
Set up CloudFront
In order to set up CloudFront to redirect http to https, you will need to set up a CloudFront distribution to:
- redirect http -> https
- forward all traffic to the invoke url of your ApiGateway
There some quirks to this, that I will get into later in this post
First, navigate to the ApiGateway dashboard and take note of the invoke url for your Gateway.
Next, navigate to the CloudFront dashboard and create a new CloudFront Distribution.
For Origin Domain paste in your ApiGateway's invoke URL.
For Origin Path if you are using your default stage, leave blank.
For Name, name the origin whatever you'd like.
Under Viewer Protocol Policy, check Redirect HTTP to HTTPS
Under Allowed HTTP Methods, check GET, HEAD, OPTIONS, PUT, POST, PATCH, DELETE
This Next Piece is Important!
Scroll down to Cache key and origin requests
Under Cache Policy choose CachingDisabled policy. This will prevent CloudFront from caching responses from your ApiGateway.
Under Origin request policy choose AllViewer policy. This will make CloudFront forward all headers it receives from the request to your ApiGateway. You will need this if your application uses cookies or Authorization header for AuthN/Z.
If your ApiGateway uses a custom domain, this next piece is important!
Scroll down to Settings
Under Alternate domain name (CNAME) add the custom domain that is currently assigned to your ApiGateway. If you're using ACM, choose the corresponding certificate for that custom domain.
By default, ApiGateway has CORS disabled. If CORS is disabled on your ApiGateway, DO NOT remove the custom domain configuration from your ApiGateway. The custom domain configuration should match between CloudFront and ApiGateway. This will ensure requests are not rejected by ApiGateway due to CORS.
Create the Distribution. After a few minutes, your Distribution should be deployed.
Copy your Distribution domain name, and update your DNS, that currently resolves to your ApiGateway, to instead resolve to your Distribution's domain name. It may take some time for DNS to propagate.
This should be all you need to set up CloudFront in front of your ApiGateway, in order to redirect http -> https. You can verify by navigating to your site, being sure to use the http protocol. Do this in a browser, and view the redirect in the network dev tools tab. You can also use cURL with the -L flag to follow redirects and see the redirects listed out listed out.
The important bits
Most of this is probably self explanatory. The pieces that aren't as intuitive:
- The Origin request policy MUST forward all headers received to ApiGateway. AWS has a precanned policy called AllViewer that does this, but you can also create your own. Just make sure the headers you need are forwarded to ApiGateway by CloudFront
- If CORS is disabled for ApiGateway, the custom domain configuration MUST exist on both the CloudFront distribution and the ApiGateway. Otherwise, ApiGateway will reject the request.
Hopefully this was helpful!

